In our fast-paced and demanding lives, one aspect that often takes a backseat is sleep. We live in a society that glorifies busyness, but what many fail to realize is that quality sleep is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. Additionally, it’s important to understand how un – healthy sleep habits and not getting enough sleep can affect your nutrition.
At Healthy Steps Nutrition, we focus on a holistic approach to nutrition, and sleep is one of the major components we work on with our clients because of its effect on nutrition.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the profound importance of sleep, delve into the art of creating a sleep routine, and discuss how to optimize your sleep environment for ultimate well-being.
What Does It Mean To Have Healthy Sleep Habits?
Healthy sleep habits, also known as practicing good sleep hygiene, involve adopting behaviors and routines that contribute to consistently obtaining high-quality sleep. These habits are essential for overall well-being and are crucial in promoting physical and mental health.
So many things can be done to help create healthy sleep habits. Doing so results in getting enough sleep. But before we go into how to create these healthy sleep habits, we must first understand why sleep health is so important. Afterall, we hear of so many people almost glorifying they can live on very little sleep. Many people have trouble falling asleep, and others put off going to bed at a decent hour for watching TV or looking at other devices.
Why Is Sleep Important?
Sleep is a fundamental and essential aspect of human life, crucial to overall health and well-being. The importance of sleep extends far beyond simply feeling rested; it encompasses various physiological, cognitive, and emotional functions.

Here are key reasons why sleep is critically important:
Physical Restoration:
During sleep, the body undergoes essential repair and restoration processes. Tissues and muscles are repaired, energy is restored, and the immune system is strengthened, contributing to overall physical health.
Cognitive Function:
Sleep is closely linked to cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and problem-solving. Adequate sleep supports optimal brain function, enhancing creativity, decision-making, and learning abilities.
Emotional Well-being:
Sleep plays a crucial role in emotional regulation and mental health. Lack of sleep is associated with mood swings, increased stress levels, and a higher risk of developing mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Hormonal Regulation:
Sleep influences the balance of key hormones, including ghrelin and leptin (related to appetite), insulin (related to blood sugar regulation), and cortisol (related to stress). Disruptions in hormonal balance due to insufficient sleep can lead to weight gain, impaired metabolism, and increased stress.
Immune System Support:
Adequate and quality sleep is essential for a robust immune system. During sleep, the body produces and releases cytokines, which are proteins that help fight inflammation and infection. Lack of sleep can compromise the immune system’s ability to defend against illnesses.
Cardiovascular Health:
Chronic lack of sleep has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension and heart disease. Quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Metabolic Health:
Sleep plays a role in regulating metabolism, and insufficient sleep is associated with an increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Lack of sleep can affect insulin sensitivity and lead to imbalances in blood sugar levels.
Memory Consolidation:
Sleep is vital for memory consolidation, the process by which the brain strengthens and stores memories. Quality sleep enhances memory, whether it’s learning new information or retaining experiences from the day.
Physical Performance:
Athletes and individuals engaged in physical activities benefit from adequate sleep, contributing to improved physical performance, faster recovery, and enhanced coordination.
Overall Well-being:
Ultimately, the overall well being of an individual is closely tied to their sleep patterns. Quality sleep contributes to a better mood, increased resilience to stress, and an improved sense of overall happiness and contentment.
How Much Sleep Do We Need?
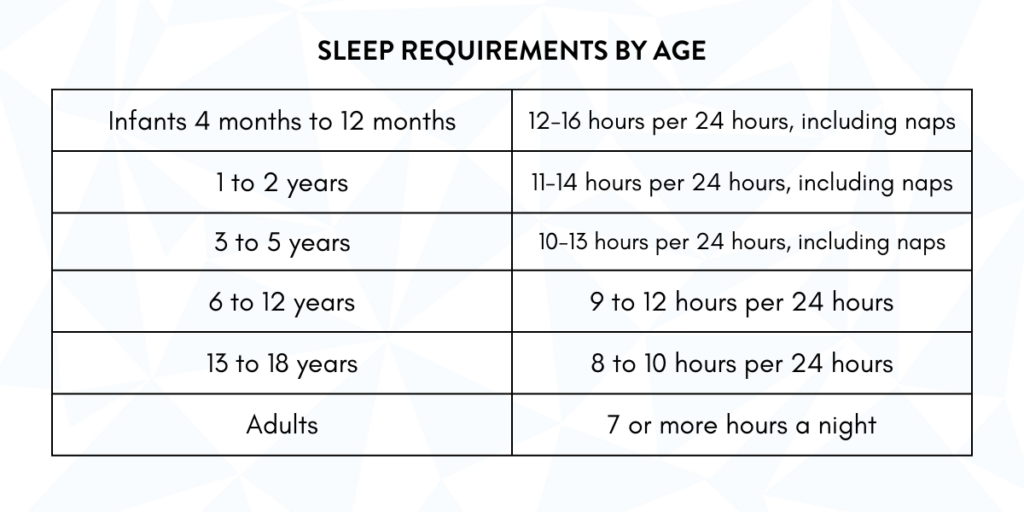
Now that we understand why a good night’s sleep is important, how much sleep do we need to say we got a good night’s rest? I know many people that fall asleep at night really well, but have trouble sleeping through the night.
Most adults need at least seven to eight hours of sleep per night. Every age group is different regarding how much sleep each night is needed. Check out the table below to help determine when you should go to bed in order to get better sleep.
How Does Lack Of Sleep Affect Nutrition?
Lack of sleep can significantly impact hormonal regulation, particularly hormones related to appetite and metabolism.
Here’s a breakdown of how insufficient sleep affects essential hormones and, in turn, influences appetite and nutrition choices:
Ghrelin (the hunger hormone)
Increase: Insufficient sleep is associated with an increase in ghrelin levels. Ghrelin stimulates appetite and promotes the feeling of hunger. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more ghrelin, making you more prone to feeling hungry even when you don’t need to eat.
Leptin (the satiety hormone)
Decrease: Conversely, insufficient sleep is linked to decreased leptin levels. Leptin signals satiety and tells your brain that you’ve had enough to eat. When leptin levels drop, it can lead to an impaired feeling of fullness, making it more challenging to regulate food intake.
Insulin
Impaired Sensitivity: Sleep deprivation can lead to insulin resistance, meaning your body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Poor insulin sensitivity also affects the body’s ability to use glucose for energy effectively.
Cortisol
Elevated Levels: Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, tends to increase with insufficient sleep. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite, particularly for high-calorie and sugary foods. This can contribute to unhealthy food choices and weight gain over time.
Impact on Food Choices and Nutrition

The food choices you make can be effected by lack of sleep. And in turn, your nutrition choices can effect how you sleep. Don’t worry! Getting into a healthy routine of good sleep habits, is only a few steps away – so keep reading!
Lack of sleep effects nutrition choices in these ways:
Cravings for High-Calorie Foods:
The hormonal changes induced by sleep deprivation may lead to cravings, especially for foods high in carbohydrates, fats, and sugars. These cravings are often driven by the body’s need for quick energy to compensate for fatigue.
Increased Snacking:
Higher ghrelin levels and reduced leptin levels can increase snacking, especially during late-night hours. This can contribute to a higher overall caloric intake, potentially leading to weight gain.
Preference for Processed Foods:
Sleep-deprived individuals may be more inclined to choose processed convenience foods high in calories, sugars, and unhealthy fats. These food choices can negatively impact overall nutrition, further increasing sleep problems.
Disrupted Meal Timing:
Irregular sleep patterns can also disrupt meal timing, leading to inconsistent eating habits. This irregularity can further affect the body’s metabolism and energy balance.
Strategies for Healthy Eating Despite Sleep Deprivation

Obviously, the point of this article is to help you establish healthy sleep habits. However, we all have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep from time to time. Regardless of the reason, here are some tips to eat healthy despite when we feel sleepy.
Mindful Eating:
Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues. Practice mindful eating to avoid overeating and make healthier food choices.
Balanced Meals:
Aim for balanced meals that include a mix of proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. This helps stabilize blood sugar levels and promotes satiety.
Hydration:
Stay hydrated, as dehydration can sometimes be mistaken for hunger. Drinking water throughout the day can support overall well-being.
Setting Up A Sleep Routine For Healthy Sleep Habits

A sleep routine will help your brain establish it’s wind-down period. Circadian rhythm is a thing that your body uses to dictate when you should be sleeping or awake.
Here are some healthy sleep habits that will help you establish a sleep routine:
1. Consistent Bedtime
Establishing a consistent bedtime is the cornerstone of a healthy sleep routine. Our bodies have internal clocks, and sticking to a regular sleep schedule helps synchronize these circadian rhythms, promoting better sleep quality.
2. Wind Down Rituals
In the hour leading up to bedtime, engage in calming activities that signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include reading a book, practicing relaxation exercises, or gentle stretching. Avoid stimulating activities, such as intense workouts or screen time, during this period.
3. Optimize Your Sleep Environment
Ensure your bedroom is conducive to sleep. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows, keep the room cool and dark, and make sure it’s quiet. Use blackout curtains and white noise machines to create an ideal sleep environment.
4. Limit Stimulants Before Bed
Caffeine and nicotine are stimulants that can interfere with sleep. Aim to avoid these substances in the hours leading up to bedtime. Learning to avoid alcohol is also a good practice.
Instead, opt for calming herbal teas that promote relaxation and improved sleep.
Wrap Up
In a world that values hustle, it’s crucial to recognize that sleep is not a hindrance to success but a cornerstone of it. By understanding the profound impact of sleep on our physical and mental well-being, creating a consistent sleep routine, and optimizing our sleep environment, we pave the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Which sleep tips are you going to follow from this article?





